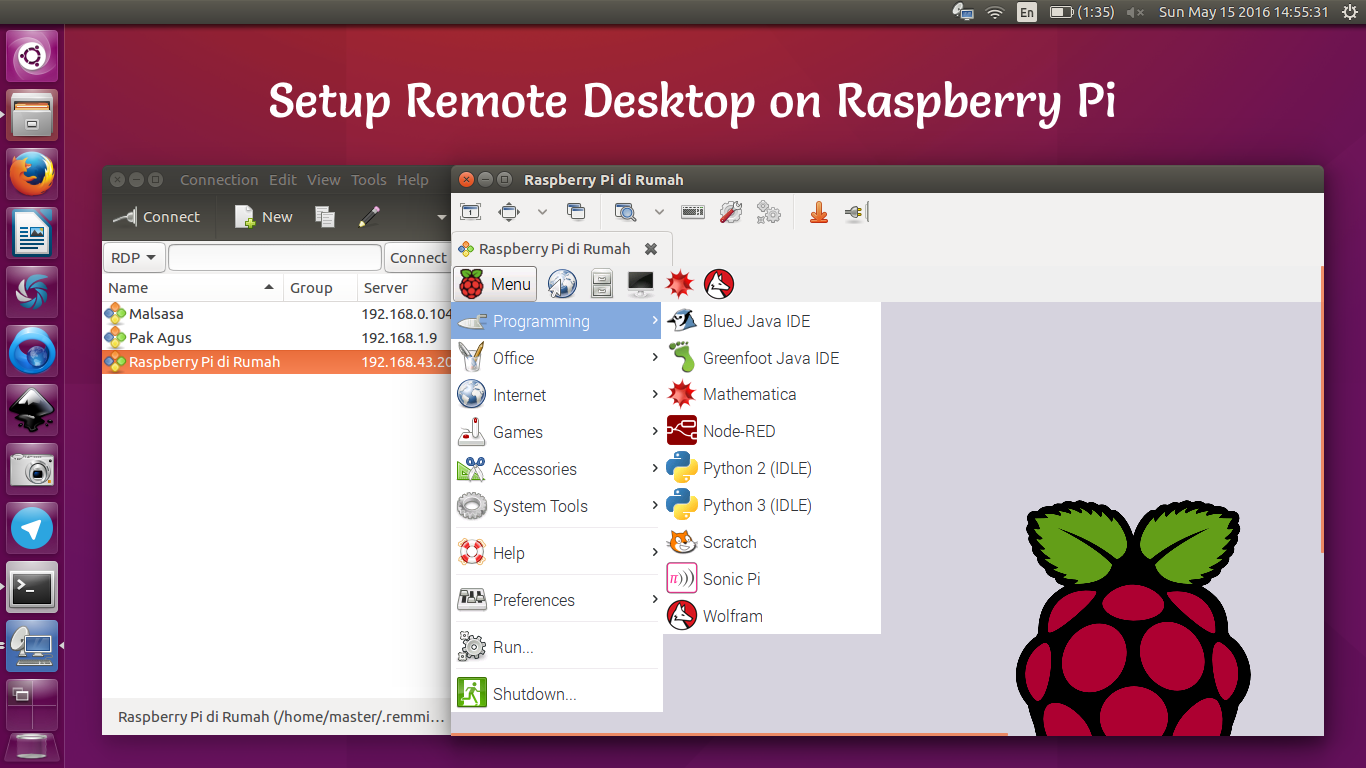
Connecting remotely to a Raspberry Pi is an essential skill for anyone working with this versatile device. Whether you're managing a home server, running IoT projects, or simply accessing your Raspberry Pi from another location, remote connectivity offers convenience and efficiency. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about setting up and optimizing remote connections to your Raspberry Pi.
As more people adopt remote work setups and explore home automation, the ability to remotely control devices like the Raspberry Pi has become increasingly valuable. By mastering remote connection to Raspberry Pi, you can streamline your workflow and unlock new possibilities for your projects.
In this article, we'll delve into the various methods and tools available for establishing secure and reliable remote connections. From basic setup instructions to advanced configurations, we'll ensure you have all the information you need to get started.
Read also:Miley Simmons A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Understanding Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
Before diving into the technical aspects, it's important to understand what remote connection to Raspberry Pi entails. At its core, remote connection allows you to access and control your Raspberry Pi from another computer or device, even when they're not in the same physical location.
This setup is particularly useful for:
- Managing headless Raspberry Pi installations (no monitor or keyboard).
- Accessing files and applications on your Raspberry Pi remotely.
- Monitoring and controlling IoT devices connected to your Raspberry Pi.
By leveraging remote connection technologies, you can efficiently manage your Raspberry Pi without being physically present, saving time and effort.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Connection
Before you can establish a remote connection, your Raspberry Pi needs to be properly configured. Follow these steps to prepare your device:
Step 1: Install Raspberry Pi OS
Ensure that your Raspberry Pi is running the latest version of Raspberry Pi OS. This operating system includes built-in support for remote connection tools, making setup easier.
Step 2: Enable SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is one of the most common methods for remote access. To enable SSH on your Raspberry Pi:
Read also:Understanding The Meaning Of Watch Atm And Its Significance In Modern Finance
- Open the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool.
- Navigate to the "Interfaces" tab.
- Select "Enabled" for SSH.
Step 3: Connect to Wi-Fi
If you plan to access your Raspberry Pi over the internet, ensure it's connected to your Wi-Fi network. You can configure Wi-Fi settings through the Raspberry Pi desktop interface or by editing the wpa_supplicant.conf file.
Methods for Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
There are several methods you can use to connect remotely to your Raspberry Pi. Below are some of the most popular options:
VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
VNC allows you to remotely control the graphical interface of your Raspberry Pi. It's ideal for tasks that require a visual interface, such as running applications or managing files.
SSH (Secure Shell)
SSH provides command-line access to your Raspberry Pi. It's lightweight, secure, and perfect for tasks like managing files, running scripts, and configuring settings.
Web-Based Interfaces
Some applications, like Home Assistant or Pi-hole, offer web-based interfaces that allow you to manage your Raspberry Pi through a browser. This method is convenient for users who prefer a graphical interface but don't need full desktop access.
Securing Your Remote Connection
Security is paramount when setting up remote connections. Follow these best practices to protect your Raspberry Pi:
- Use strong, unique passwords for SSH and VNC.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible.
- Regularly update your Raspberry Pi OS and installed software.
- Restrict SSH access to specific IP addresses if feasible.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful setup, issues can arise when trying to establish a remote connection. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
Problem 1: Unable to Connect via SSH
Ensure that SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi and that your firewall settings allow SSH traffic. Double-check your IP address and port number.
Problem 2: Slow Connection Speeds
Optimize your network settings and consider using compression with SSH to improve performance. Additionally, ensure your Raspberry Pi has sufficient resources to handle the connection.
Problem 3: VNC Connection Fails
Verify that VNC is installed and running on your Raspberry Pi. Check for any conflicts with other remote access tools and ensure your VNC client is up to date.
Advanced Configurations for Remote Connection
Once you've mastered the basics, you can explore advanced configurations to enhance your remote connection experience:
Port Forwarding
Set up port forwarding on your router to allow access to your Raspberry Pi from outside your local network. This requires careful configuration to maintain security.
Dynamic DNS
Use a Dynamic DNS service to assign a domain name to your Raspberry Pi's IP address. This makes it easier to connect, especially if your IP address changes frequently.
SSH Tunnels
Create SSH tunnels to securely forward traffic between your local machine and Raspberry Pi. This method is particularly useful for accessing services that aren't natively secure.
Tools and Software for Remote Connection
Several tools and software can facilitate remote connections to your Raspberry Pi:
RealVNC
RealVNC is the official VNC client for Raspberry Pi and offers a seamless remote access experience. It supports both local and internet-based connections.
Putty
Putty is a popular SSH client for Windows users. It's lightweight, easy to use, and provides robust SSH functionality.
TeamViewer
TeamViewer is a versatile remote access tool that supports both SSH and VNC connections. It's user-friendly and suitable for beginners and advanced users alike.
Best Practices for Efficient Remote Connections
To maximize the efficiency of your remote connections, follow these best practices:
- Optimize your Raspberry Pi's resources by closing unnecessary applications.
- Use compression to reduce data transfer times over SSH.
- Regularly back up your Raspberry Pi's files and configurations.
- Document your setup process for future reference.
Real-World Applications of Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
Remote connections to Raspberry Pi have numerous real-world applications:
Home Automation
Use your Raspberry Pi to control smart home devices remotely. You can monitor and adjust settings from anywhere, ensuring your home remains comfortable and secure.
Remote Server Management
Configure your Raspberry Pi as a lightweight server and manage it remotely. This setup is ideal for hosting websites, running applications, or providing file storage.
IoT Projects
Monitor and control IoT devices connected to your Raspberry Pi from a remote location. This capability is crucial for projects involving environmental sensors, security systems, and more.
Conclusion
Remote connection to Raspberry Pi opens up a world of possibilities for managing and interacting with your device. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can set up secure and reliable remote connections tailored to your needs.
We encourage you to experiment with different methods and tools to find the best solution for your projects. Don't forget to share your experiences and insights in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more tips and tricks related to Raspberry Pi and remote connectivity.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Connection
- Methods for Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
- Securing Your Remote Connection
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Advanced Configurations for Remote Connection
- Tools and Software for Remote Connection
- Best Practices for Efficient Remote Connections
- Real-World Applications of Remote Connection to Raspberry Pi
- Conclusion